ALS
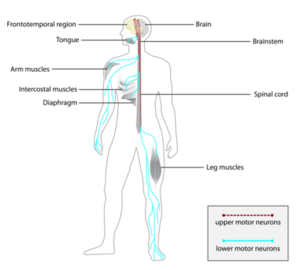
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, also known as motor neuron disease or Lou Gehrig's disease, is a rare, terminal neurodegenerative disease defined by the progressive loss of both upper and lower... Wikipedia
- Symptoms: Early: Stiff muscles, muscle twitches, gradual increasing weakness, Late: Difficulty in speaking, swallowing, and breathing, respiratory failure, Rare: frontotemporal dementia
- Complications: Falling, Respiratory failure, Pneumonia, Malnutrition
- Usual onset: 45–75 years
- Causes: Unknown (90% to 95%) or genetic (5% to 10%)
- Risk factors: Genetic risk factors, age, male sex, heavy metals, organic chemicals, smoking, electric shock, physical exercise, head injury
- Diagnostic method: Clinical diagnosis of exclusion based on progressive symptoms of upper and lower motor neuron degeneration for which no other explanation can be found. Supportive evidence from electromyography, genetic testing, and neuroimaging
- Differential diagnosis: Multifocal motor neuropathy, Kennedy's disease, hereditary spastic paraplegia, nerve compression syndrome, diabetic neuropathy, post-polio syndrome, myasthenia gravis, multiple sclerosis
- Treatment: Walker, wheelchair, non-invasive ventilation, feeding tube, augmentative and alternative communication, symptomatic management
- Medication: Riluzole, edaravone, tofersen, dextromethorphan/quinidine
- Prognosis: Life expectancy highly variable but typically 2–4 years after diagnosis
- Data source: DuckDuckGo